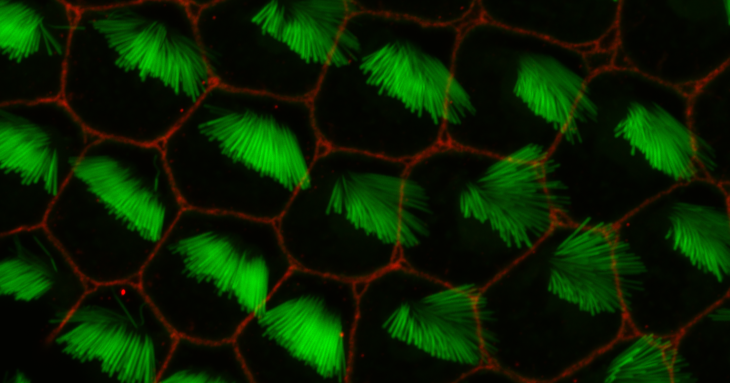
-
Professor P. V. Shivaprasad receives the 2025 Tata Transformation Prize
Dr. Padubidri V. Shivaprasad, Professor at the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS), Bengaluru is the Food Security Winner for Tata Transformation Prize 2025. The prize entails a research grant of INR 2 crores (approximately USD 228,000) to advance their research and support real-world implementation.
-
Dr. Anjana Badrinarayanan wins Infosys Prize 2025 in Life Sciences
We are delighted to share that Dr. Anjana Badrinarayanan, faculty member at NCBS–TIFR, has been awarded the Infosys Prize 2025 in Life Sciences.
-
NCBS and ICTS Announce the Establishment of CALIBRE – Centre for Artificial Learning and Intelligence for Biological Research and Education
The National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) and the International Centre for Theoretical Sciences (ICTS), both centres of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), have signed an agreement to jointly establish a Centre for Artificial Learning and Intelligence for Biological Research and Education (CALIBRE).
-
Dr Deepa Agashe awarded the Rashtriya Vigyan Yuva Puraskar 2025 by the Government of India
Dr Deepa Agashe, Associate Professor at the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS-TIFR), Bengaluru, is the recipient of the Rashtriya Vigyan Yuva Puraskar 2025, conferred by the Government of India.
Link to the Announcement: https://awards.gov.in/
Link to Dr Deepa Agashe's lab webpage: https://adaptationlab.in/
-
A new way to watch bacteria modify our proteins in real time
Bacteria have evolved many clever ways to take over human cells during infection.
-
Ecological Factors Determine The Evolution of Antipredator Strategies of Animals
A walk through a forest can be a bewildering experience. The whole forest appears to be running wild with insects of varied colours, hues and behaviours. Many of these traits appear to be deployed in defense against visually-hunting predators such as birds and lizards. Evolutionary biologists have long puzzled over the factors that determine when animals evolve to deter predators either through striking visual displays or by hiding in plain sight (i.e., camouflage).
-
NCBS' research on National Geographic: The curious case of the tigers who changed their stripes
National Geographic has released a major cover story on the pseu
-
How does a species fight extinction?
In the 1990s, when Kauai crickets in Hawaii sang love songs with their wings to attract mates, a new island visit
-
How do cells build organs without a blueprint?
For cells to form functional organs, they must not only multiply but also migrate to the correct loc
-
A new database to predict protein function without complete 3D structural information.
Proteins drive nearly every process within a cell.