-
When worms go with the flow of physics
Worms may look simple, but the way they move through the world is anything but.
-
Sometimes, do nothing - genes respond better when they wait
When a cell receives a signal (like a hormone), it needs to turn specific genes on quickly and precisely.
-
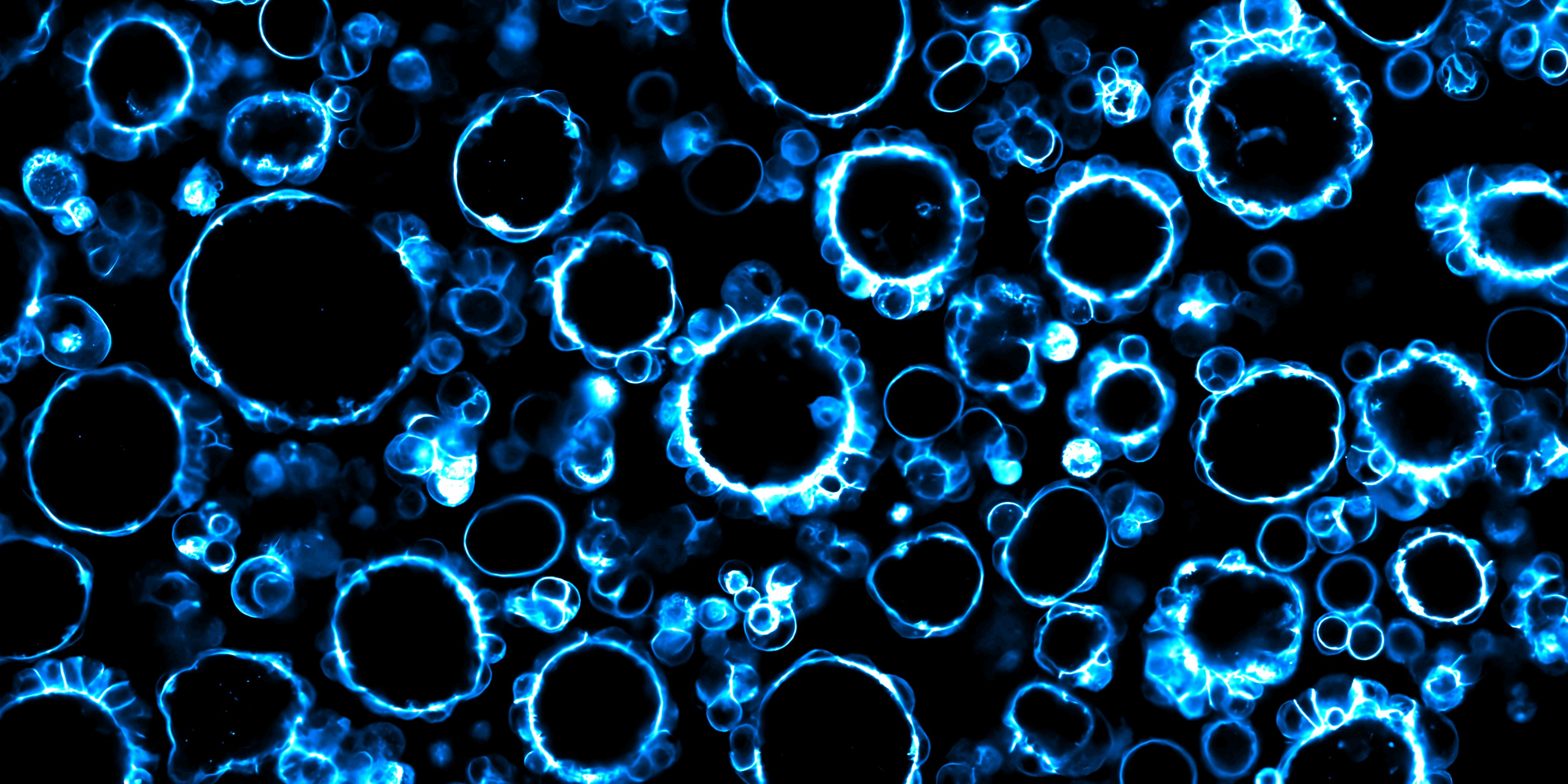
How chemistry controls cancer cell clusters
Cancer cells are often imagined as rogue agents growing uncontrollably.
-
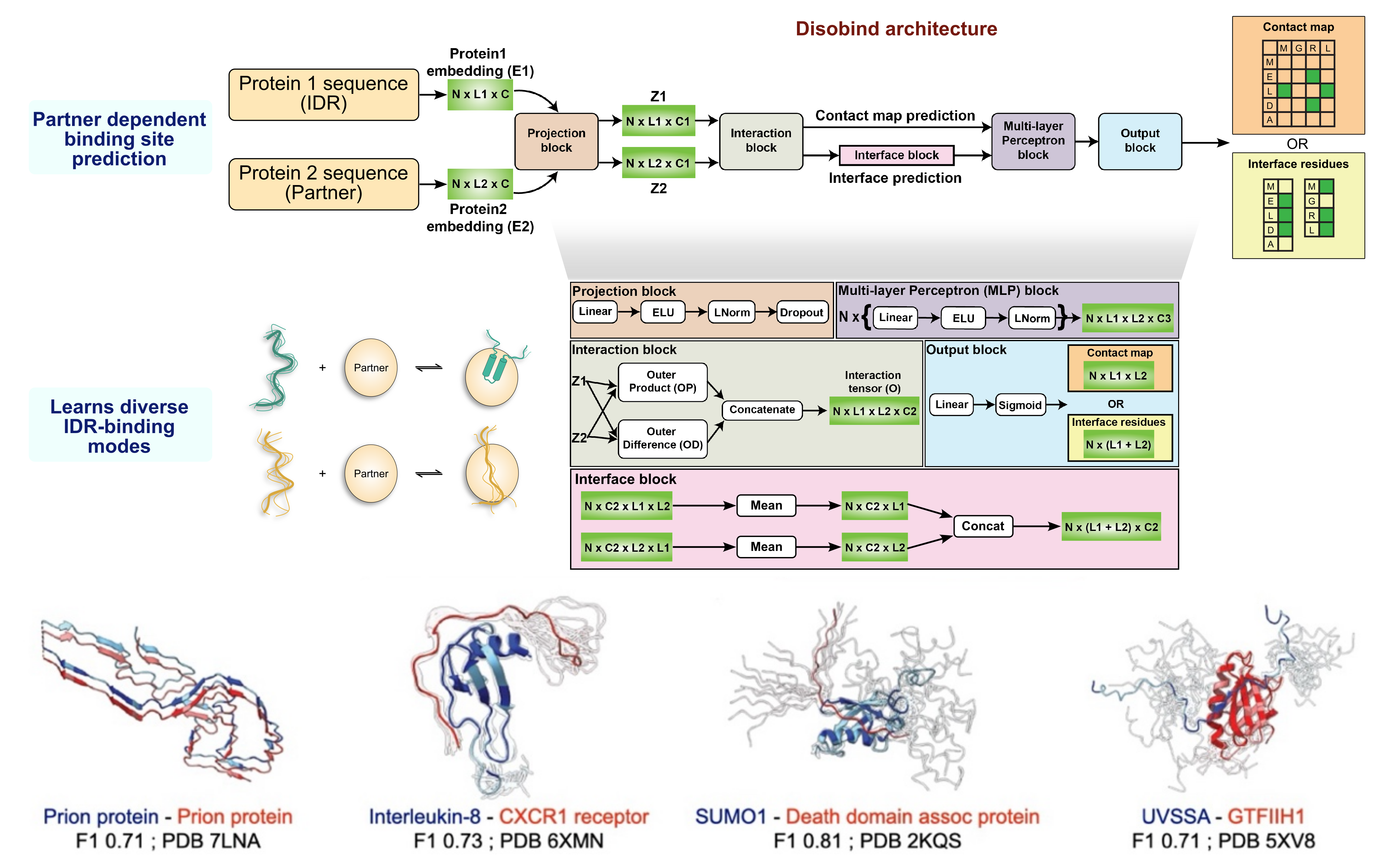
How scientists predict what shapeless proteins do
Proteins are not always neatly folded molecular machines with a fixed shape that determines what they do inside
-
How muted neurons in the human brain could be made to chatter again : treatments for brain disorders
The brain of any living organism, in general, is composed of millions of tiny cells called neurons.
-
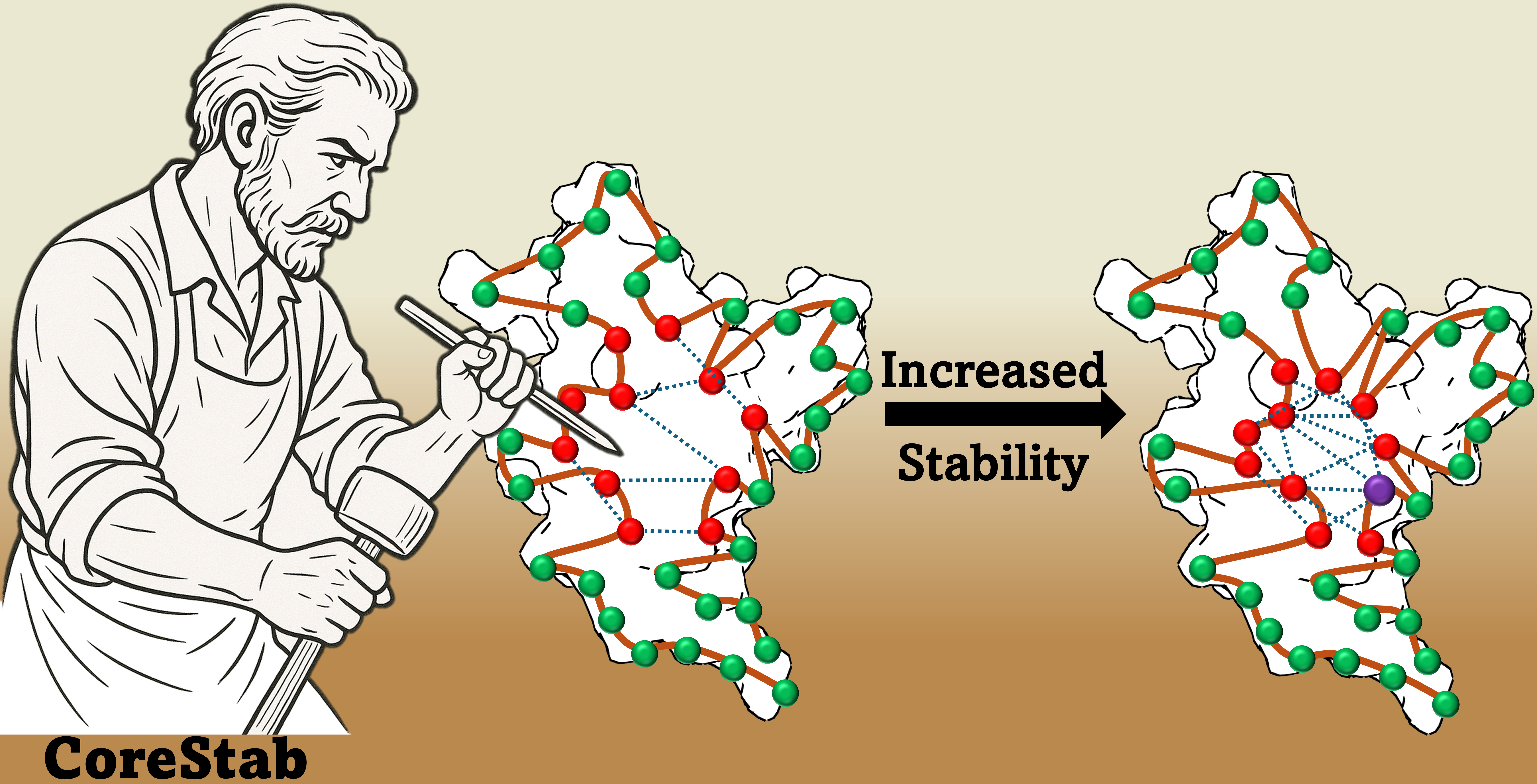
Mind the gaps! Proteins do better when packed tight
Proteins are essential for life - from immune signalling to digestion, almost every biological process relies o
-
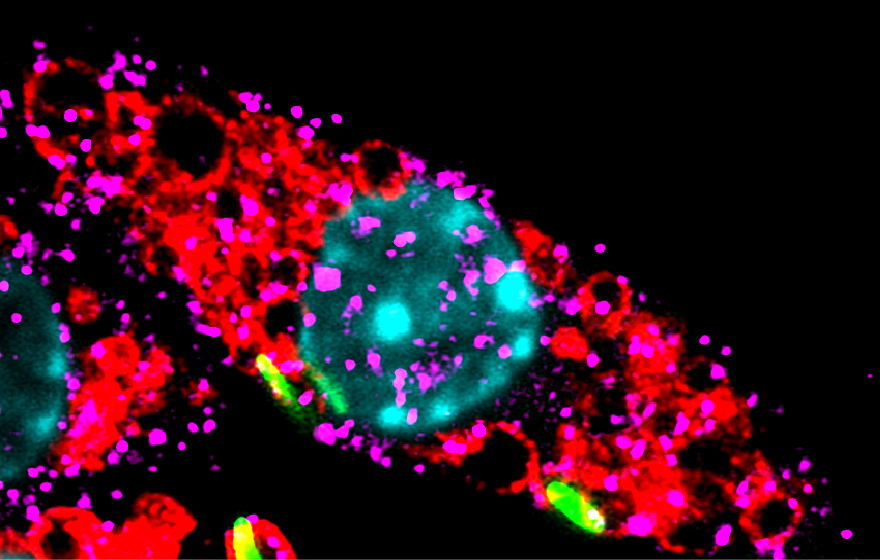
How Tuberculosis turns our defences against us
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the world’s oldest and deadliest diseases, which takes a toll on over a million peo
-
Rice uses a single molecular switch to heal after injury
When a rice leaf is torn or bitten, the plant doesn’t just sit still. It launches a series of rapid molecular alarms.
-
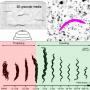
A new way to watch bacteria modify our proteins in real time
Bacteria have evolved many clever ways to take over human cells during infection.
-
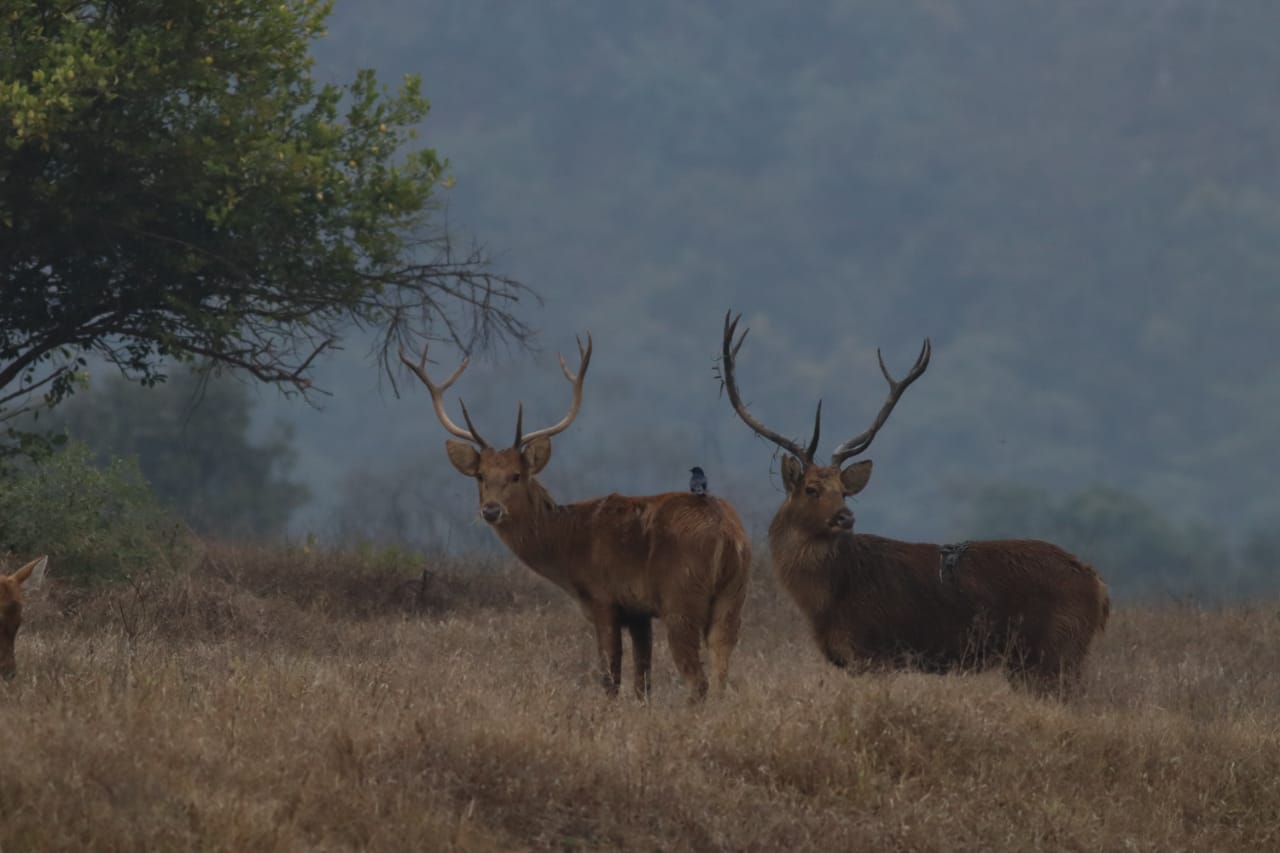
Village relocations redraw the wildlife map
When Project Tiger was launched in 1973, efforts to carve out safe havens for tigers took on a new urgency.