-
When close physical contacts are good, and guilt free
Image description: Line drawing of the Drosophila head showing the compound eye (pink). Individual repeating units of the compund eye are seen and individual cellular structures superimposed in each unit. Image credit: Dr. Deepti Trivedi.
Imagine diving into a eukaryotic cell.
-
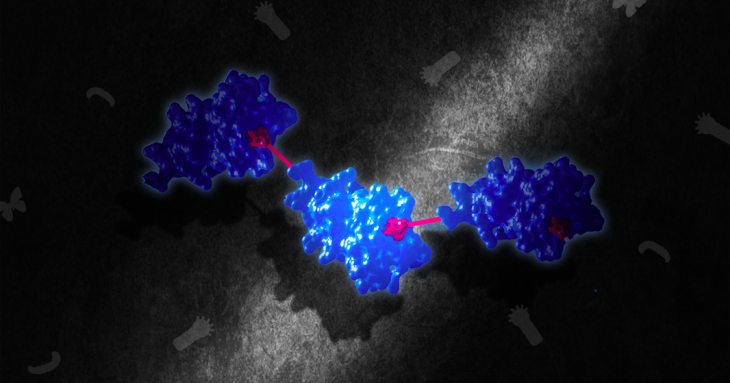
‘Cyclotides’ from Shankhpushpi can fight bacteria, virus, say Bengaluru-based scientists
In a new study that was published in Scientific Reports, a team of researchers from the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) studied the functioning of special circular proteins in plants called “cyclotides”, which the pharma industry uses ...
-
Micromanaging calcium levels in neurons: From flies to humans
Calcium is as vital to neurons as musical notes are for a song. Levels of calcium oscillate like crescendos, regulating neuronal communication, function and survival. Also, much like cringing to wrong notes, calcium imbalance is seldom tolerated by neurons. In fact, derailed cellular calcium levels are a harbinger of certain neurodegenerative disorders in humans. Hence to regulate calcium traffic, neurons harbor vigilant protein passages and compartments.
-
In Memoriam: Shri R.D. John
It is with deep sadness that we acknowledge the passing of Shri R.D. John on the morning of 26 July 2020.
-
SARS-CoV-2 genome sequencing effort
COVID-19 response by scientists at DBT-inStem and NCBS-TIFR, Bengaluru
-
An extra topping of Lysine and why it matters to Baculovirus Ubiquitins
Proteins often use Ubiquitin tags to be shuttled within cells or dispatched for degradation. Although small in demeanor, Ubiquitins are hugely influential.
-
NCBS welcomes new faculty member: Shaon Chakrabarti
The National Centre for Biological Sciences is delighted to welcome Shaon Chakrabarti, who joins the Centre as its newest faculty member.
Shaon’s research combines theory and experiments to study cellular proliferation at the single cell level -- its underlying physical principles, control mechanisms, and consequences in development and disease. The eventual goal of his research is to build on these basic principles to improve therapeutic strategies in the clinical treatment of cancer. -
Professor Sumantra Chattarji elected a lifetime member of the EMBO
The BLiSC community congratulates Prof. Sumantra Chattarji on his election as a lifetime member of the EMBO in recognition of his remarkable achievements in the life sciences.
-
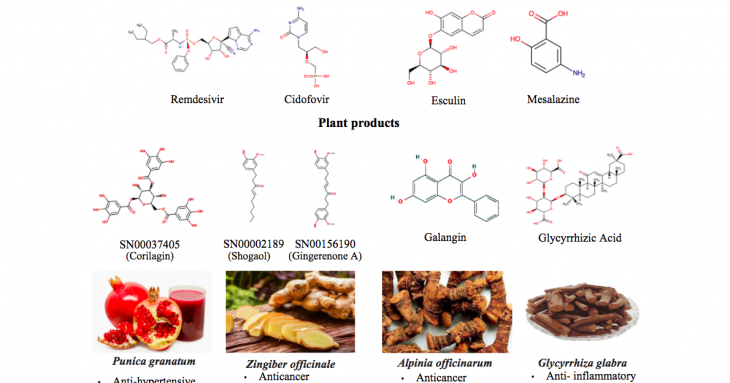
Needle in a haystack: Computational search narrows down COVID-19 cure possibilities
Along with the those on the frontlines, thousands of researchers around the world are working to identify the right approach to tackling the COVID-19 pandemic from various angles and disciplines. The search for effective treatment options and vaccinations for the SARS-CoV-2 has occupied scientists and medical researchers in recent months in an unprecedented manner.